Deep sea technology : Tools For Research
Technology has almost invaded all parts of the world. It has spread like a virus. It breathes underwater too. For over two decades now, NOAA’s NURP (NOAA’s Undersea Research Program) has revolutionized underwater research world. It has specialized not only in developing but also modifying and operating advanced underwater technologies. It has enabled Nation’s scientists to accomplish broad spectrum of research work.
Some of the tools that has enabled such progress are SCUBA diving, Submersibles, remotely operated vehicles etc. The NURP- funded research supports NOAA’s responsibilities towards oceans, coasts and great lakes with the help of advanced research technologies. NURP supports scientific research that addresses NOAA's management responsibilities through a rigorous peer-review process patterned after the National Science Foundation. To be successful, The OER Ocean Exploration and Research (OER) creates the capabilities within the scientific departments which involves dedicated staff to establish prior formalities based upon priorities for investment by working with future users of the technologies. This involves researching and monitoring advancements made by other agencies, institutions, academies and the industry. The OER takes the responsibilities for executing the investments through mechanisms such as grant, contracts. They also ensure that proven technologies are executed smoothly into operations. This in fact is also referred to as “end-to-end” technology development process.
Scuba Diving
SCUBA diving is an exciting and first-hand way for scientists to study the underwater environment. It is one among the most effective ways for executing underwater experiments that require high quality precise measurements. SCUBA as the name suggests stands for Self Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus. It literally means that all divers carry all of required breathing equipments and gases with them. Hence they are subjected to water temperature, pressure, currents, and other factors revolving oceans present at the diving depth.

The NURP program approximately supports about 10,000 SCUBA Divers for Scientific Research work. NURP provides all the necessary equipments and finances for scientists and technical assistance to conduct diving operations. They use both open circuit as well as closed circuit breathing apparatus. The difference between them primarily relies upon what happens to the exhaled gas. In open system the gas is exhaled in to the water. A closed system apparatus has recycling abilities and thus lasts longer underwater as it reduces carbon-dioxide and adds oxygen in a cyclic manner inside the container. It reduces the amount of gas required in the container and also allows the diver to remain streamlined.

The breathing gas provided by NURP involves compressed air, NITROX and TRIMIX. NITROX is a composition of nitrogen and oxygen whilst TRIMIX is a composition of oxygen, nitrogen and helium. NITROX is of special interest to NOAA. It was in introduced in late 1970’s which allows the divers to stay longer underwater when compared to compressed air alone. Each of these gases is of different properties which enables the diver to dive at maximum depths. The NOAA Dive Manual (4th Edition) produced through the collaboration of NURP and NOAA Marine and Aviation Operations, which operates the NOAA Dive Program offers a high quality precise review about the diving equipments, gas mixtures, First-Aid, Marine Life and Brief history of Diving. Want to learn more info about Scuba Diving Technolgy. Click Here...
Deepsea Habitats
Divers do have some limitations that can inhibit their productivity. Factors such diving depth, gas mixture, weather and decompression obligations can have a significant impact on scientist’s research work. The more times spent underwater for research work can also raise financial constraints.
Saturation diving on the other hand has proven to be useful for extending their research time spent underwater. It works accordingly as, if a diver’s tissues are in equilibrium with the surrounding water, then the decompression time will not end change for the length time spent underwater. The time taken for attaining saturation in saturation diving is about 24 hours and thus a diver can eventually spend 24 hours underwater continuously. The development undersea habitat which is also known as undersea laboratories has made saturation diving a reality for divers and scientists for conducting better experiments. The undersea habitat is a pressurized facility that allows the divers to extend their depth ranges and depth times. Aquarius in the Florida keys national marine sanctuary, at a depth of 63 feet allows divers to undergo compression or decompression in the undersea habitat or a surface chamber.
Aquarius is the only undersea habitat in the world devoted to science. NURP provides the abilities to live and work beneath the waves in this laboratory. The habitat is owned by NOAA and operated by the South-eastern and Gulf of Mexico center, is located three miles of Key Largo at a depth of 64 feet. It is at the base of coral reef within the Florida Keys national marine sanctuary, an ideal place for studying the eco-systems. For a 10 day mission, the habitat can accommodate 4 scientists and 2 technicians. The Aquarius has supported over 80 missions from 1993 to 2003. Want to learn more info about Deepsea Habitats. Click Here...
Human Occupied Submersibles

Scientists can be physically transferred to greater depths of the ocean far beyond the physiological restrictions of a diver with the help or submersibles. NURP has a variety of submersibles available. Namely Pisces 4 and Pisces 5 operated by Hawaii & West Pacific regional center carry one pilot and two scientists each. They are capable of diving around 2000 meters. It is custom equipped to accommodate a variety of requirements. Standard gear includes eternal video and still cameras, 2 hydraulic manipulator arms, CTD profiler and color sonar. Pisces 5 is 220 feet. JSL known as Johnson-Sea-Link is owned by the Harbor Branch Oceanogra0-pphic Institution (HBOI) and leased to NURP scientists for research work.

Thanks to its fish bowl acrylic sphere, 2 scientists can make experiments at 3000 feet underwater. Delta submersible has 19 viewing ports and can reach a depth of up to 1100 feet. It is owned and operated by Delta Oceanographic. The submersible is pretty small that it can be carried around in a plane to research site across the world. Alvin is a 3 person submersible vehicle (DSV) with a capability of reaching depths such as 14,450 feet. Owned by U.S.Navy and operated by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute (WHOI) and funded by National Science Foundation (NSF), National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the Navy. It has taken about 8300 people underwater of which 4000 are deep sea divers and have been on missions for about 20,000 hours underwater. Want to learn more info about Human Occupied Vehicle. Click Here...
Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs)

Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROV’s) are unmanned robots. They are controlled by pilots via a long tether spooled out from the support ship. They can have extra fittings such as advancement cameras, lighting and sampling systems. Allows scientists to be virtually transported through a real time video transmission to greater depths. The advantages are greatly extended bottom times, reduced human risks, affordable technology, abilities to be deployed in harsh environments. NURP operates a number of ROV’s. ROV’s has been used to conduct science in a wide range of experiments from tropics to the poles.

Kraken owned by the center of North Atlantic and Great Lakes at university of Connecticut is one such ROV. It is a light vehicle with a depth capacity of about 3000 feet. The manipulator arm in them allows the pilot to pilot around, gather specimens for further observations and analysis. Its suction samplers collect organisms and sediments. The cameras installed in them allow high resolution, wide angles and close up color images illuminated by 400 watts of HMI lighting. A low monochromic camera can be used to view organisms that are sensitive to bright lights. A digital 35mm camera with flash facilities allows still photographs to be taken. Paired lasers allow the scientists to estimate the size and scale of the objects underwater. Scanning Sonar uses sound to view objects and organisms outside the visibility range of cameras and light equipments installed on board.
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs)

Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV’s) forms a part of most recent class of undersea research technologies. It is independent of the surface, battery powered, controlled by super computers with the help of artificial intelligence. They are used to conduct various measurements, video surveillance tasks. The REMUS AUV was developed by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution for NURP’s Mid-Atlantic Bight Center to perform wide area continental shelf surveys.
Sea Water to Drinking Water
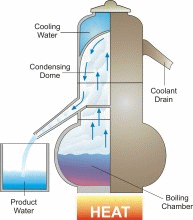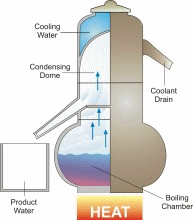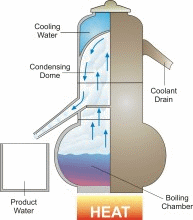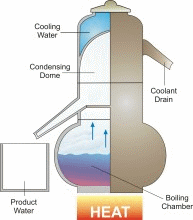
Humans cannot drink saline water. But saline water can be made into fresh water which is required by everyone. 70% of our human body consists of water. That shows why water plays a key role for our survival. The process of converting salt water into sea water is known as desalination. US has great access to several water supplies for drinking purposes but still with the ever growing population shortage of water occurs more often in certain locations whilst in certain other locations salt water is converted into fresh water for drinking. The optimum method to desalinate salt water is by reverse osmosis. But thanks to its high cost its being used pretty rarely. Reverse osmosis per acre foot for desalination costs about 1000$ compared to normal water supply sources who cost 200$ for the same acre foot. However desalination technology is improving and prices are falling. Tempa Bay, FL is currently desalinating water at 650$ per acre foot. As the demand for technology and fresh water increases more desalination procedures are more likely to happen, especially in areas such as California and Middle East.
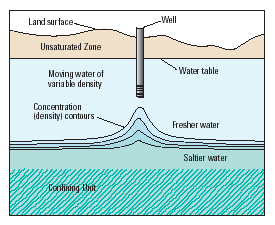
Saline water is water that contains large amounts of dissolved salts. This concentration is the amount of salt (by weight) in water expressed as ppm (parts per million). Say if a water has 10,000ppm of dissolved salt in it, then 1% of the weight of the water comes from them.
Parameters for Saline Water:- Fresh Water - Less than 1000 ppm
- ArrowSlightly Saline Water - 1000 to 3000 ppm
- ArrowModerately Saline Water - 3000 to 10,000 ppm
- ArrowHighly Saline Water - 10,000 to 35,000 ppm.
 Deep Sea Crabs
Deep Sea Crabs