Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean which separate Asia from the Americas. The Pacific Ocean is the biggest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from Arctic in the north to Antarctica in the south, bounded by Americas in the east and Asia and Australia in the west. The equator subdivides it into the North Pacific Ocean and South Pacific Ocean, with two exceptions: the Galpagos and Gilbert Islands are deemed totally within the South Pacific.
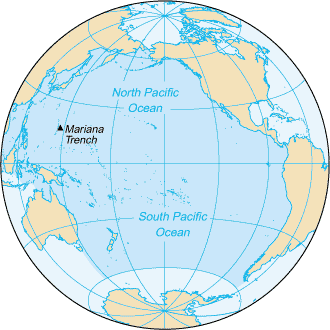
At 169.2 million square kilometres (65.3 million square miles) in area, this biggest division of the World Ocean - and, in turn, the hydrosphere - covers about 46% of the Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, making it larger than all of the Earth's land area combined. The Mariana Trench in the western North Pacific is the deepest point in the World and in the Pacific, reaching a depth of 10,911 metres.
Location
Body of water between Southern Ocean, Asia, Australia, and the Western Hemisphere.
Geographic coordinates: 0 00 N, 160 00 W.
Climate
Planetary air pressure systems and resultant wind patterns exhibit remarkable consistency in the south and east, trade winds and westerly winds are well-developed patterns, modified by seasonal fluctuations, tropical cyclones (hurricanes) may form south of Mexico from June to October and affect Mexico and Central America, continental influences cause climatic consistency to be much less pronounced in the eastern and western regions at the same latitude in the North Pacific Ocean, the western Pacific is monsoonal - a rainy season occurs during the summer months, when moisture-laden winds blow from the ocean over the land, and a dry season during the winter months, when dry winds blow from the Asian landmass back to the ocean, tropical cyclones (typhoons) may strike southeast and east Asia from May to December.
 Deep Sea Crabs
Deep Sea Crabs