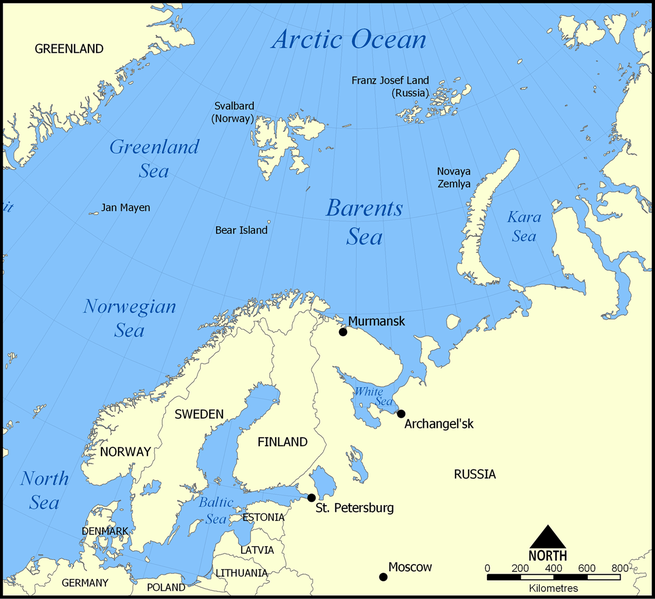
Barents Sea
The Barents Sea is a part of the Arctic Ocean, lies to the north of Norway and Russia.
Geography
It is quite deep shelf sea, with average depth of 760 feet (230 m) and maximum depth of 1,480 feet (450 m) , surrounded by the shelf edge towards the Norwegian Sea in the west, the island of Svalbard (Norway) in the northwest, and the islands of Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya (Russia) in the northeast and east. Novaya Zemlya separates the Kara Sea and the Barents Sea.
Naming: The Sea is known as Murman Sea in the middle Ages, the current name has come from the Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz. Resources: Fossil fuel energy is the significant resources exist in the Barents Sea region.
Climate
In winter, the average of air temperature 13° F (-25° C) in the north and 23° F (-5° C) in the southwest, while in summer 32° F (0° C) in the north and 50° F (10° C) in the southwest. Annual precipitation in the south is 20 inches (500 m) but only half of that in the north. The southern part of the Barents Sea, including the ports of Murmansk (Russia) and Vardø (Norway) remains ice-free year round due to the warm North Atlantic drift. In September, the entire Barents Sea is more or less ice-free.
Three main types of water heaps in the Barents Sea:
- warm , salty Atlantic water (temperature > 3°C, salinity < 35) from the North Atlantic drift,
- Cold Arctic water (temperature > 0"C, salinity < 35) from the north,
- Warm, but not very salty coastal water (temperature >3°C, salinity<34.7)
Oil and Gas
Slow development in oil and gas, due to the costs and political risks involved. The Russian side contains a number of large gas fields in upper Jurassic sandstone reservoirs; while in Norwegian side contains smaller middle-lower Jurassic sandstone reservoirs. List of fields in Norway are Snøhvit (Snow white) field, Johan Castberg field and Goliat field. Fields in Russia are Shtokman field, Prirazlomnoye field, Ludlovskaya field, Murmanskoye field and Ledovoye field.
Ecology
Because of the North Atlantic drift, it contains the world largest cod population. Haddock and capelin are the famous feed deep-sea. Feeding fishes like catfish, plaice, herring, and salmon. Some invertebrates like shrimplike crustaceans, bivalves and sponges. There are also Land mammals like polar bear and Arctic foxes, seal mammals like seals and whales. In warm weather we can see ducks and geese. It contains 20 to 40 percent of lichens, mosses and shrubs..
 Deep Sea Crabs
Deep Sea Crabs